When designing a silo plant, it is very important to consider that it should:
- Be compact and operational.
- Be flexible, allowing alternative processes.
- Have open spaces and access, in view of future expansion.
- Allow the automation of processes, such as grain drying.
- Have low operating costs (staff, electricity, fuel).
- Have a low impact on the environment.
Besides, when designing the sections it should contain, you have to bear in mind 4 fundamental steps:
1. Reception. Sampling, weighing and discharging.
2. Conditioning. Pre-cleaning, cleaning and drying.
3. Storage. Storage silos (insect control, humidity and temperature).
4. Dispatch. Loading trucks or wagons, weighing, sampling and preparation of documentation.
Layout
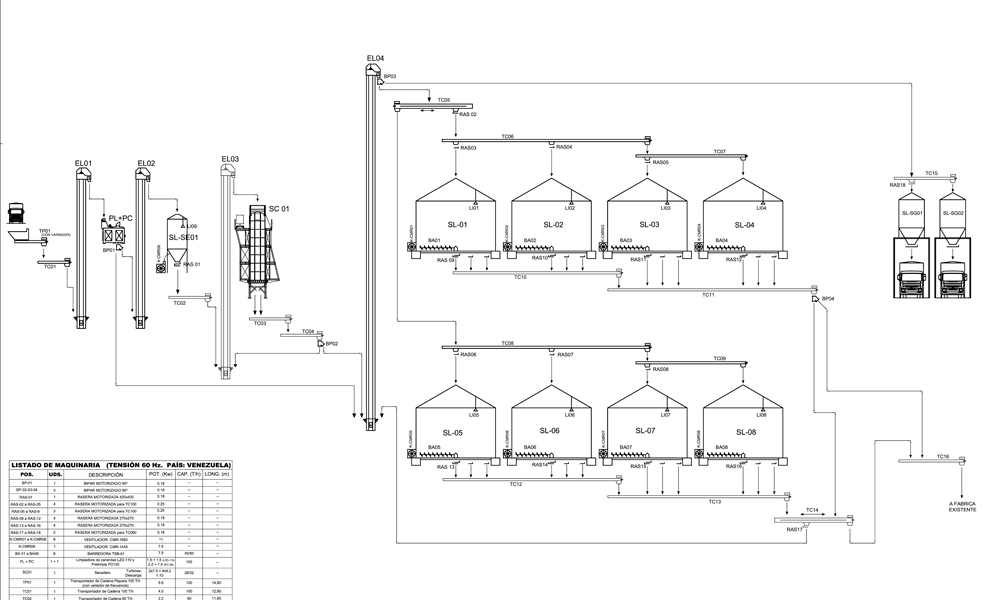
This layout includes the following elements:
- RECEPTION: intake pit
- CONDITIONING: pre-cleaning and drying
- STORAGE: storage silos, with ventilation and thermometry.
- DISPATCH: silos for bulk cargo truck.
This plant does not include tempering silos, which are placed after the dryer when the harvested grain has a high degree of humidity. Its function is to help the dryer in the drying process at peak harvest. Nor does it include buffer silos, standing before the dryer, with the aim of separating the wheat according to its moisture content and giving time for the dryer to make the drying process.



Do you have detail specificaion for 12000T maize silo
Thanks for your request. You will receive the information by email.
Best regards